The break-even point is reached when. Determining the break-even point
Many companies use various analytical techniques, including those borrowed from abroad, to manage their income and costs. Among them, the simplest and most common is CVP analysis, which involves estimating the break-even point. By learning to make simple calculations, you can get an effective financial management system with elements of strategic planning.
Break even
Break-even point (BEP)– sales volume at which the entrepreneur’s profit is zero. Profit is the difference between income (TR – total revenue) and expenses (TC – total cost). It is measured in physical or monetary terms. It helps determine how many products need to be sold (services performed) to cover costs. At the break-even point, revenues cover expenses. If it is exceeded, the company makes a profit; if it is not achieved, the company incurs losses.
Dear reader! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to know how to solve exactly your problem - contact the online consultant form on the right or call by phone.
It's fast and free!
It represents a mathematical and graphical assessment of the relationship between three main components:
- WITH– enterprise costs.
- Q– quantity of products sold (in natural units).
- Pr- profit.
All calculations are made with the aim of:
- determine the physical and cost volume of sales, which will allow not only to compensate, but also to obtain the desired profit;
- predict what profit can be obtained if the sales volume is known;
- assess how profit will react to changes in price, costs or quantity of goods;
- establish the optimal structure for this type of activity.

Where to start?
You must first decide which costs are fixed and which are variable, since they are mandatory components for the calculation.
The main condition for conducting CVP analysis is the division of all enterprise costs into two groups:
Variables(VC – Variable Cost) – costs, the volume of which changes in proportion to the increase (decrease) in production volume. That is, the more products you need to produce, the more you will have to spend, and vice versa. These usually include raw materials and supplies, semi-finished products, workers’ wages, fuel and electricity for technological purposes, packaging, etc.
The average variables are calculated separately ( AVWITH– Average Variable Cost), which show the size of VC per unit of production. Over time, their size does not change.
Permanent(FC - Fixed Cost) - costs, the change of which does not directly depend on the growth and decline in production volumes. These are, as a rule, the costs of maintaining administrative personnel, utility bills, communications, depreciation, etc. All these costs will occur even if the company cannot produce or sell anything. In this sense, they are conditionally constant.
Calculation formula
Break-even point is calculated in two dimensions:
In natural units:
VERNAT = FC / (P – AVC) = FC x Q / (TP – VC)
Where P is the price.
This determines the minimum acceptable sales volume in physical units of weight, length, volume or quantity.
In monetary units:
VERDEN = VERNAT x P
This determines the amount of revenue that will cover and make zero profit.
There is another method for calculating BER in monetary terms. But for this you need to use the indicator marginal income/profit (MR– Marginal Profit). It characterizes the part of the proceeds that will remain after financing variable costs and will be subsequently used to cover fixed costs and make a profit.
MP = TP – VC = FC + Pr
Average contribution margin will be calculated like this:
AMP = MP / Q = P – AVC
Marginal income ratio – This is the share of marginal income in the company's revenue. It shows how many kopecks of profit each additional ruble of revenue will bring.
K MP = MP / TP = AMP / P
Then to calculate the break-even point in monetary terms you can use the formula:
BEP = FC / K MP
The need for calculation
Break-even analysis – an important source of information for making decisions regarding business activity:
- Should you invest in a specific project? For an entrepreneur, it is important not to “burn out” and it is important to know from what point the risk of financial failure will decrease. Based on the BER indicator, you can calculate the volume of sales, starting from which a new business will begin to make a profit, and investments will pay off.
- What does the change in BELIEVES over time indicate? Expansion and contraction of activities directly affects the level of the critical point. The larger the size of the company, the higher its VER. But if the volume of activity has not changed, and the profitability threshold has become higher, this may signal problems. Something goes wrong if you have to sell more than before to make a profit.
- Change price or sales volume? The BEP indicator contains a linear relationship between the price and quantity of goods intended for sale. On this basis, a strategic decision is made: if the selling price changes, how much should the sales volume be changed in order not to lose profit? And vice versa, how should the pricing policy be adjusted in the face of changes in the scale of sales?
- How much can you afford to reduce revenue and still break even? The BER indicator is used when calculating the financial safety margin ( MFS– Margin of financial safety), which directly answers the question posed.
MFS = (TP – BEP) / TP x 100
MFS is determined as a percentage and allows you to compare different enterprises with each other. This coefficient is a kind of airbag. The higher it is, the better the company’s financial position is protected from any negative changes in the market.
Calculation examples
Although all enterprises use the same formulas for calculating BEP, the industry and type of activity influence the composition of costs, as well as their division into VC and FC.
For the store
Trading enterprises have a wide range of products with different price characteristics, so it is physically impossible to calculate the critical volume for each type of product. It is more expedient to calculate the VER for the outlet as a whole. To do this, we conditionally divide costs into variable and fixed.
By selling goods worth more than 1,012,500 rubles, the store will make a profit, and revenue below this level will plunge the outlet into losses. In this state of affairs, each additional ruble of revenue brings 40 kopecks of profit.
For enterprise
Manufacturing enterprises that specialize in the production of homogeneous products can calculate the critical point in both natural and monetary units.
Indicator Amount
Sales volume, pcs. 10,000
Sales price, rub. 150
Revenues from sales(p.1 x p.2) 1 500 000
Variables: 1 000 000
Raw materials and supplies 800,000
Salary of main workers with deductions 100,000
Electricity for technological purposes 40,000
General production expenses 60,000
Average variable costs (p. 4 / p. 1) 100
Marginal income(p.3 – p.4) 500 000
Fixed costs: 187 000
Factory overhead costs 62,000
Depreciation and repair of equipment 25,000
Utility bills (gas, electricity, water, electricity) 30,000
Salary of management and maintenance personnel with deductions 70 00
Profit(p.6 – p.7) 313 000
Break-even point in natural units(p. 7 / (p. 5 – p. 2)) 3 740
Break-even point in monetary units(p. 9 x p. 2) 561 000
At this enterprise, making a profit is possible already from a sales volume of 3,740 units or 561,000 rubles.
Certain assumptions when calculating
The calculation is simple and universal, but has its own conditional limitations (assumptions):
- the selling price does not increase with an increase in the volume of units sold;
- costs remain unchanged;
- Products are sold completely (without any leftovers in the warehouse or in production) in one operating cycle;
- VER calculation is made for one type of product for which the cost can be determined.
Limitations make the BER indicator not an absolute, but a conditional indicator and causes criticism from many analysts.
VER schedule
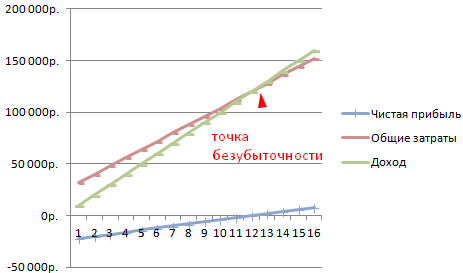
An important method of analysis is visual, which involves constructing a break-even chart.
Since BER is the level of activity at which income is equal to costs, the break-even point on the graph is formed at the intersection of two graphs: income (TR) and total costs (TC). The projection on the Q axis will show the size of BER in physical terms, and on the TP axis - BEP in monetary terms.
Since there are fixed costs even with zero sales volume, the TC schedule starts from a point equal to the size of FC.
Sequence of plotting:
- An income graph is being built: the first point is at 0, and the second is at the intersection of sales volume in physical units and the amount of revenue.
- A cost schedule is constructed: the first point on the vertical axis is at the level of fixed costs, and the second at the intersection of sales volume in physical units and total (fixed and variable) costs.
- At the intersection of the graphs, VER is marked, as well as the profit and loss area.
CVP analysis is a methodology that is easy to understand and apply, which will enable entrepreneurs to control current costs, plan prices and volume of activities that ensure profit. Only by understanding the relationship between the main indicators can you learn to manage them.
Entrepreneurs who are planning to open a store or buy a ready-made one are concerned about how much and at what pace they need to sell in order to cover losses and reach profit. To do this, the break-even point (TB) is calculated - that is, a state in which costs are equal to income and net profit is zero. Let's look at the most common ways to calculate this indicator.
Break-even point: by eye
Let’s assume that 80 thousand rubles are spent on renting premises per month, 60 thousand rubles on salaries to sellers, 18 thousand rubles on insurance premiums, 10 thousand rubles on utilities, 800 thousand rubles on purchasing goods.
The markup in the store is 25%. We sum up all the expenses and divide them by the markup. We calculate the sales volume at which expenses equal income:
(80 + 60 + 18 + 10 + 800)*1000/25% = 3 million 872 thousand rubles.
To reach the break-even point, you need to earn at least 3 million 872 thousand/30 ≈ 13 thousand rubles per day.
By marginal income
The following data will be required:
- Fixed expenses (Fpost), which include rent, communications, security, utilities, salespersons’ salaries, contributions to insurance, salary and pension funds, taxes and advertising costs,
- revenue (B);
- variable costs for the full volume (Rper),
are calculated using the formula: Sales volume (Or)*Average purchase price of goods (PP)
To calculate your break-even point, you will need systematic data on expenses and income. With the Business.ru program you can receive detailed cash flow reports and carry out the necessary calculations to determine the effectiveness of your business. You can use the program's functionality remotely at a time convenient for you.
First, we calculate the marginal income (DM). This is the delta between revenue and variable costs: MD = B - Rper.
Then we calculate the value of the break-even point in monetary terms: TBden = Rpost / Kmd
For example, revenue is 1.5 million rubles, variable expenses are 700 thousand rubles, and fixed costs are 155 thousand rubles per month.
(1) MD = 1,500,000-700,000 = 800,000 rubles
(2) Kmd = 800,000/1,500,000 = 0.53
(3) TBden = 160,000/0.542 = 292,452 rubles.
Consequently, the store will begin to make a profit when sales exceed 292,452 rubles.
Calculation per unit of goods
When you are just starting a business or occupying a new niche in the market, you cannot always calculate the marginal income for the entire volume of goods sold. In this situation, you can use the values of the purchase and sale prices:
MD/unit = ZTs-TsR, where TsR is the selling price of a unit of goods.
The marginal income ratio is calculated as follows:
Kmd = MD/unit/PC.
TBden = Rpost / Kmd
How to calculate your break-even point
Break-even point: chart
You can determine the break-even point using the chart. To do this, you will need the level of fixed costs, the average purchase and sales price.
Two curves are constructed: the first - all costs (Рп+Рpost), the second - sales revenue. The point at which they intersect is the desired quantity.
Break-even point: online
Those who do not like to bother with tables, calculations and graphs can use a calculator on the Internet (http://allcalc.ru/node/759).
It is enough to enter fixed costs, costs per unit of goods, volume of units, selling price into the appropriate cells and click calculate. The calculator itself will calculate the break-even point.
A program for optimizing the work and financial reporting of a Business.Ru store will allow you to maintain full-fledged financial, warehouse and trade records. At any time convenient for you, you can receive reports on expenses, costs per unit of goods, number of units, selling price and much more.
Direct costing
Let’s say our store presents positions A, B, C and D:
|
(t.r.dec. ) |
R lane (t.r.dec. ) |
R post (t.r.dec. ) |
|
Let’s use the methods from direct costing and calculate the range of break-even points.
TBden=Рpost/(1-Kr.per), where Kr.per is the share of variable costs in revenue,
Kr.per = Rper/V.
We will also calculate the marginal income for each product and its share in revenue.
|
(t.r.ub.) |
TOR. lane |
||
The break-even point reflects the volume of production, sales of goods and services, which covers all costs of the enterprise. In an economic sense, it is an indicator of a critical situation when profits and losses are zero. This indicator is expressed in quantitative or monetary units.
The lower the break-even point of production and sales volume, the higher the solvency and financial stability of the company.
Break-even point formula in Excel
There are 2 ways to calculate the break-even point in Excel:
- In monetary terms: (revenue * fixed costs) / (revenue - variable costs).
- In natural units: fixed costs / (price – average variable costs).
Attention! Variable costs are taken on a per unit basis (not total).
To find breakeven, you need to know:
Fixed costs (not dependent on the production process or sales) - rent payments, taxes, salaries for management personnel, leasing payments, etc.
Variable costs (depending on production volumes) - the cost of raw materials and materials, utility bills in production premises, workers' salaries, etc.
Selling price per unit of goods.
Let's enter the data into an Excel table:
- Find the volume of production at which the company will receive a net profit. Establish the relationship between these parameters.
- Calculate the volume of sales of goods at which the break-even point will occur.
To solve these problems, we compile the following table with formulas:

- Variable costs depend on the volume of products produced.
- Total costs are the sum of variable and fixed costs.
- Income is the product of production volume and product price.
- Contribution margin is total revenue minus variable costs.
- Net profit is income without fixed and variable production costs.
Let’s fill out the table and see at what output the enterprise will be “in the black.”

Starting from the 13th production, net profit became positive. And at the break-even point it equals zero. Production volume – 12 units of goods. And the income from sales is 120,000 rubles.
How to graph the break-even point in Excel
To clearly demonstrate the economic and financial condition of the enterprise, we will draw up a graph:
- We decide on the appearance of the graph and click the “Select data” button.
- For demonstration, we need the columns “Total Costs”, “Revenue”, “Net Profit”. These are the elements of the legend - “Rows”. We manually enter the “Row Name”. And in the “Values” line we make a link to the corresponding column with data.
- The range of horizontal axis labels is “Production Volume”.
We get a graph like:
Let's change the graph (chart layout) a little.

This demonstration allows us to see that the net profit at the break-even point is indeed “zero”. And it was after the twelfth release of the product that “plus” began.
Where are such calculations needed?
The “break-even point” indicator is in demand in economic practice to solve the following problems:
- Calculation of the optimal price for the product.
- Calculation of the amount of costs at which the company still remains competitive.
- Drawing up a product sales plan.
- Finding the volume of output at which profitability will appear.
- Analysis of the financial condition and solvency of the enterprise.
- Finding the minimum production volume.
Ready-made calculations and templates for analyzing an enterprise's break-even point.
The profitability threshold, or break-even point, is the volume of products/services sold, upon reaching which the company covers all its expenses, but does not yet have a profit. Using this indicator, you can calculate whether the chosen methods of production growth are suitable for the enterprise and how sustainable the course of development is.
The last parameter allows you to record the moment of financial stability, that is, when the sales volume exceeds the minimum profitability. Next, the term “break-even point” and methods for calculating it will be discussed in detail.
What is the break-even point
The break-even point is the volume of sold products/services at which the resulting profit (not to be confused with income) changes from a negative value to zero.
Best article of the month
We have prepared an article that:
✩will show how tracking programs help protect a company from theft;
✩will tell you what managers actually do during working hours;
✩explains how to organize surveillance of employees so as not to break the law.
With the help of the proposed tools, you will be able to control managers without reducing motivation.
Profit is calculated by deducting all expenses from the company's income. There are two types of break-even point:
- in kind;
- in monetary terms.
The break-even point is determined to establish the quantity of products/services with the sale of which income and expenses will become equal. Naturally, this applies to a situation where initially expenses were greater than income. As a result, after exceeding the break-even point, the business becomes profitable. In contrast to this state, the business operates in the negative until the equilibrium ratio has not yet been achieved in the company.
The break-even point shows how stable the company's financial position is. And if this value grows, then this is a sign that the company has difficulties in generating income.
At the same time, the break-even point is not fixed; its data changes in relation to the growth of the enterprise. And its value is influenced by many factors - growth in trade turnover, opening of new branches, changes in pricing, etc.
The break-even point, in turn, affects a number of positions in the company.
- If this indicator is calculated correctly, it can be seen whether it is reasonable to invest in the project given the current state of finances.
- This parameter identifies problems in the company that affect changes in its value.
- When establishing the break-even point and the volume of sales required by the company, it becomes clear how much it is necessary to increase or decrease the quantity of products sold, the scale of production, subject to a revision of their cost. In the opposite situation, it is possible, on the contrary, to identify the impact of changes in production volume on price formation.
- The break-even point shows to what minimum limit the company's profit can be reduced, but at the same time still maintain positive work, without losses.
A graph that allows you to clearly see the appearance of the break-even point
Expert opinion
Correct 6 mistakes that prevent your company from increasing profits by the end of the year
Oleg Braginsky,
founder of the School of Troubleshooters, director of the Braginsky Bureau
After half the year has passed, interim results are usually summed up and an analysis of the company’s work, its achievements and failures is carried out. We must remember that there are still six months for profits to grow and, at the end of the year, to be profitable. But there are some mistakes or incorrect actions that can prevent this from happening. The main ones can be seen in the checklist (see appendix), and the 6 main mistakes are as follows.
Mistake 1. Annoying monotonous actions.
A company can constantly do the same things - find customers only through the sales funnel, not listen to customers to create a more customer-friendly atmosphere, continue to interact with consumers through different channels instead of creating a unified one. At the same time, all departments are separated, each working on its own - advertising, service, and sales.
For example, in the middle of winter, a buyer came to one of the agricultural holdings on the b2b market to purchase fertilizer. The head of the enterprise, in the process of communicating with a client, who turned out to be the director of a state farm, learned that the latter got to the holding’s website thanks to the Internet. He made the purchase, and after that the marketing specialists of the agricultural holding began to attack him regularly, sending emails and communications over the network and offering tools, fertilizers, or seedlings. The client did not like this, it caused irritation, since unnecessary goods were offered, and fertilizers were offered at the wrong time. Marketers had to take into account the information received from customers, make advertising targeted and retain this customer.
Clients do not like it when the same identical actions are performed against them with enviable regularity. To prevent this from happening to you, over the next six months actively communicate with customers at all stages of cooperation. Otherwise, your customers will go to your competitors.
A good solution would be to use Client Journey Map (CJM). McKinsey claims that B2B firms using CJM experience a 10% increase in profits. CJM helps to look at the process through the eyes of the buyer, to outline and apply the customer experience. To do this, perform the following analysis:
- marketing channels that the client used when he first contacted your company;
- what exactly the person liked about the site;
- what the customer asked you before making a purchase;
- what products, services, what promotions are of interest to the client;
- what did not suit the customer during the purchase, what objections did you encounter.
Client Journey Map translated from English is called a client journey map and is a technology in the field of marketing that allows you to make working with consumers as simple as possible, increase their loyalty to the company, and help them interact with your company.
To obtain the data necessary to implement all of the above, your employees must constantly note all the moments and processes of a client’s contact with the company. To do this, you should install a CRM system, set up a website and all communication technologies:
- record all information about clients that is available;
- write down in the scripts the questions that the sales employee should ask first-time applicants;
- combine data about what steps a customer takes on your website with the actions of salespeople working with customers coming from the sales funnel.
This way, you can see the user's journey from their first visit to making a purchase. It is worth breaking down customers into sectors depending on how similar their behavior is. And for each group, draw up a map, best in the form of a diagram or graph, which will show all the moments of contact between customers and your company and their response actions. In the future, the information obtained can be used for clients with similar behavior.
This method will allow you to combine the efforts of different departments of your company, because with the joint activities of the marketing and sales departments and their use of complete information, the results of work will only improve.
Mistake 2. Insufficient detail in the buyer persona.
Customers in companies are usually divided into existing, former and new. But more detailed differentiation is not carried out, plus this principle will not apply to sellers, but in vain. Consumer behavior differs not only according to the specified criteria, but also depending on the region in which they live, on which manager they communicate with, and at what stage of the purchase they are at. And the same criteria apply to sellers. Taking these nuances into account will help maintain customer loyalty and improve service.
To solve this problem, it is worth starting from the scope of your company’s activities and its mission. When setting a goal to increase sales in certain territories, it is advisable to detail the list of clients according to the following parameters:
- their location;
- what kind of purchases they make in this area;
- Which sellers are they most willing to contact and make purchases with?
This will make it clear what the client looks like in a particular region. And based on this portrait, potential buyers can be offered exactly the products that are most likely to interest them. At the same time, it is worth assigning to the client exactly the manager whom he sympathizes with, because this will help increase sales. In this case, the client will see that you have high-quality service and that he is valued in your company.
If the company’s current goal is to improve the work of sales managers, then the following approach can be used. Specialists should be divided into groups. For example, some of them do a better job with male customers, while others do a better job with female customers. To organize work, incoming calls must be addressed to the administrator, who will distribute them to the most suitable sellers depending on the gender of consumers.
Taking into account exactly this information allows you to retain customers and increase sales. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze data on the behavior of buyers and sellers and choose the right managers to work with a particular customer.
Mistake 3. Not being interested in the opinions of customers.
When creating new types of products/services, a company usually focuses on its own views, and not on the wishes of customers or their needs.
That is, in most cases, no one asks clients for their opinions or listens to the feedback they voice. As a result, the company produces products that are not in demand and are inconvenient for customers. It is imperative to listen to the wishes of large clients. Let there be at least one full meeting with your most important customers.
A solution might be to invite your highest-earning clients to a meeting of sorts at least once a year. If this year you have not yet collected the opinions and feedback of your customers for analysis, then do it as quickly as possible. As an option, you should organize a business weekend at a hotel in the city or with a trip somewhere, have a buffet and discuss your products and services with guests, ask them to evaluate your company’s service, business development, find out their opinion about the products that you are planning release. At such a meeting you will be able to find out the following information:
- what improvements the company needs;
- what changes to make in goods being prepared for release;
- how necessary are the products already on the market, etc.
You can get this information during regular customer surveys, but the fact is that large customers like to feel appreciated and receive attention. Therefore, it is easier to achieve maximum loyalty from them by showing that their opinion as experts is important to you.
Mistake 4: Retaining customers who are no longer valuable.
Often in times of crisis, companies strive to retain any customers, despite the fact that they do not make a profit. Or, on the contrary, they are trying to attract new customers without trying to retain the old ones. However, the flow of customers requires constant attention on your part. It is worth starting to work according to the following scheme - keep profitable clients, and if they leave, then return them, and delete unnecessary ones. Before the end of the year, you need to edit your customer base according to this principle.
The solution is to retain those consumers who regularly buy your products, who have a loyal attitude towards your company and who advocate for your brand. The customer base should be divided into parts, highlighting the amount of the check, the frequency of purchases made, the presence of debt or its absence to your company.
It is worth stopping to retain those customers whose check amount and, therefore, the margin are insignificant, even if they make purchases frequently, or those who contact you very rarely. To do this, you can change the sales conditions to be more profitable for the company. For example, increase the average purchase amount. Or change the minimum order conditions from one product to several. Loyal customers will accept these conditions, and the rest will drop out.
But if you see that customers are leaving in large numbers or that you have lost your best customers, then the situation needs to be analyzed. It’s worth calling buyers from the b2b sector to find out the reasons for their dissatisfaction. If it suddenly turns out that your best clients are now working with a competitor, ask why they left and what you are missing. This question can be asked directly to customers, or you can purchase a competitor’s product for comparison. The b2b sphere allows you to return lost customers using Internet tools - email newsletters, organizing surveys, notifications about discounts and promotions, etc. You just need to focus on attracting customers who can bring profit and not be useless.
Mistake 5. Linking managers to clients.
Managers in the b2b sector usually work with their own client base. At the same time, customers do not like it when the seller changes. And managers act according to an already established scheme, often forgetting to offer new services or products. That is, you pay them for simply serving a regular customer.
To solve this problem, you can analyze the work of sellers over the past six months. And if it is clear that the client is buying the same thing and for the same amount as always, then assign another manager to him. Or you can motivate your employees by tying the receipt of a cash bonus to their performance results. In this case, understanding that his remuneration depends on the amount spent by the buyer and on the quantity of goods sold, the manager will make every effort.
Mistake 6: Content is unattractive to readers.
Today, many companies use social media - blogs, networks, and start their own channel on YouTube. But at the same time, the content posted by marketers is boring and uninteresting - ordinary reports, dry articles, speeches of directors, etc. That is, social networks are used formally, without the goal of attracting customers.
To solve this problem, you need to create interesting and non-standard content in order to get noticed. In this case, you must adhere to three rules.
- Management should not appear on social networks. Subscribers already subconsciously associate a speech or article from the director with boring content. And they need interesting and lively material to forward to their friends. Therefore, the best content would be to post photos, entertaining and educational information.
- Present your company's products or services in a unique way, from an interesting angle. You can show the production process or some unusual approach to using products. It is best to come up with at least ten such ways.
- Hire actors to produce interesting video content. Although it is more expensive, the result is worth it. Actors will be able to talk more convincingly about a company or product than ordinary employees; they will be able to convey to the audience the emotions of owning the products. Plus, such content will not only be educational, but also entertaining; it will be constantly “liked” and “shared,” especially by fans of the actors and their subscribers.
One of the basic terms that any aspiring entrepreneur needs to know is what the break-even point is. Calculating it is extremely important even at the stage of business planning, since without it it is impossible to have a full view of the future business and an understanding of the required volumes of production or provision of services. Let's look at how the break-even point is calculated, why it is needed and where it is used.
Table of contents:The concept of break-even point - why you need to determine it

In general, as an economic concept, the break-even point is a situation in which a business's profit is zero and total revenues equal total expenses. The traditional way to calculate the break-even point is to construct a graph, the horizontal axis of which represents the volume of products or services provided, and the vertical axis represents cash.
On this graph of the break-even point in the traditional format, you should draw a line of fixed costs, which is parallel to the horizontal axis, an ascending line of total expenses and an ascending line of revenue from sales of products and services. The point of intersection of the line of total expenses with the line demonstrating the income of the enterprise will be the break-even point. Accordingly, with an increase in sales volumes in comparison with the break-even point position, the company will make a profit, and if they decrease, it will suffer losses.
Important fact
In English economic theory, the break-even point is called BEP (break-even point), total expenses - TC (total cost), total revenue - TR (total revenue). In subsequent formulas and calculations, traditional English terminology will be used.
Not every modern entrepreneur is aware of the need to know the break-even point of a business. Many Russian businessmen do not have an economic education and do not even take into account such basic details that are important when opening and running their own business. Perhaps this is why the percentage of failed enterprises and closing organizations in Russia exceeds the world average.
At the same time, knowledge of the basic terms and principles of economic theory will not require any additional skills or abilities, since you can easily calculate the break-even point and build a graph in a few minutes. In general, the answer to the question “why do you need a break-even point” could be as follows:
- To determine the feasibility of a particular project as a whole. For example, in some cases, the break-even point may ultimately be completely unattainable given the existing production capabilities or volumes of services provided.
- BEP as an indicator can be used if it is regularly revalued to identify problems associated with the economic activities of the enterprise as a whole.
- Drawing up a break-even chart will allow you to visually evaluate and calculate changes in profit and the possible price of a product when sales volumes change, and vice versa - to understand how a decrease or increase in sales volumes can affect the business.
- Determining possible critical modes at the enterprise and using the break-even point as one of the markers or indicators of a crisis situation.
note
Almost always, the break-even point is a general, simplified indicator and does not always correspond to reality upon closer examination. However, this indicator makes it possible to evaluate the business, its condition and prospects as a whole, providing the basis for a subsequent deeper assessment, if there is a need for it.
How to calculate the break-even point - formulas, calculation procedure

Before starting to calculate the break-even point, it is necessary to determine all the factors and indicators that will be used in such calculations. Thus, at least the following indicators will be used in the calculations:
- FC (fixed cost) – fixed costs not related to production volumes. These include rental payments, some types of taxes and fees, utility bills (partially), employee salaries (also not in all situations), and so on.
- AVC (average variable cost) – variable costs. Such costs include the direct costs of producing one unit of product or providing one specific service. These may include, in part, the remuneration of employees, the cost of raw materials and related costs, taxes and other similar expenses.
- P (price) – the price of the final product in the form of a good or service that will be paid by the consumer.
In physical terms, the calculation of the break-even point is as follows:
BEP = F.C. ( P - AVC )The break-even point in such a calculation formula will demonstrate the required minimum quantity of products that the company needs to produce in order to reach the profit margin. Another method and way of calculating the break-even point is to determine it in monetary terms. In such a situation, the break-even formula will look like this:
BEP = F.C. /( C / P )In this case, the indicator C means the profit from the sale of one unit of product from which the total costs of its production are subtracted. The fixed costs in the formula are ultimately divided by the contribution margin ratio, which allows us to determine the break-even point as the total amount of revenue required to avoid losses when there is no profit.
Advantages and disadvantages of the break-even point as an economic tool
The break-even point is a very convenient and, most importantly, simple economic tool that allows anyone to analyze a business, including those who do not have any economic education.
At the same time, this tool allows you to draw up models of future business that are close to reality, and adjust sales plans and costs of the enterprise. However, it also has a number of disadvantages. In particular, these include:
- Failure to take into account the real dependence of fixed costs on changes in production volumes;
- Ignoring changes in the cost of an individual unit of production depending on the volume of its production;
- Lack of flexibility and consideration of possible changes in product costs within one schedule.
 Of course, these shortcomings can be partially offset by the development and construction of more complex graphical interpretations of the break-even point. However, the need to carry out complex additional calculations ultimately makes such a method inaccessible to most ordinary entrepreneurs without an economic education. Therefore, the break-even point in activities and in its analysis should be used only as one of the tools for control and verification, and not rely entirely on the application of such knowledge and its absolute correspondence to reality.
Of course, these shortcomings can be partially offset by the development and construction of more complex graphical interpretations of the break-even point. However, the need to carry out complex additional calculations ultimately makes such a method inaccessible to most ordinary entrepreneurs without an economic education. Therefore, the break-even point in activities and in its analysis should be used only as one of the tools for control and verification, and not rely entirely on the application of such knowledge and its absolute correspondence to reality.

