Demand for young professionals in the labor market. The main problems of the labor market of young specialists in the Russian Federation
Not only in Russia, but also in foreign countries, young professionals are the most socially vulnerable group of the population. Despite this, the labor market for young professionals has always been and will be the largest innovative and strategic resource states. Therefore, it is impossible not to recognize the fact that socio-economic policy is simply obliged to direct all its efforts towards recognizing this area of employment as the highest priority.
For this main goal training of qualified specialists should be of strategic importance. After all, they own the latest technologies and are perfectly adapted to the conditions of a modern market economy. Not only the growth of the country's economy, but also the future of the state as a whole depends on the achievement of this goal.
Growing unemployment in Russia is connected, first of all, with the inconsistency of the profiles and volumes of training of specialists with the requirements and needs modern market labor. That is why the rate of unemployment among graduates of professional educational institutions in the country is steadily growing every year. Today, in the employment centers of the Russian Federation, every third young specialist with a secondary or higher education has the status of unemployed. professional education, or even several.
The main tasks of the labor market for young professionals
The fulfillment of tasks for the normal functioning of this area of the labor market for the most part lies with the state. In addition, their decision should be accompanied by the help of both employers and the youth themselves. For example, the choice future profession lies with the students, and it must be carried out on the basis of its demand in the country. Everyone should think about their future and career in advance. Employers, in turn, should still provide young people with the opportunity to prove themselves, since the state of the Russian economy depends on this group of the population.
The main tasks of the youth labor market:
- Achieving an optimal balance of supply and demand in the market, which will ensure an appropriate standard of living for the main part of the population, as well as maintaining its effective stimulation.
- Optimal mobility of labor resources - educational and geographical - should be formed in the country. The state of the entire market economy of the state directly depends on the solution of this problem.
- Russia must compete in production with other countries, thereby increasing the number of vacancies in various enterprises.
- The closest correspondence between the country's production and the professional training of young specialists should be achieved.
Youth labor market and its characteristics
The characteristics of the market for young professionals differ significantly from the labor market for other population groups. At present, the youth labor market in Russia is characterized by:
- The imbalance of supply and demand in the market. It is almost impossible to find job offers for graduates without work experience.
- State support for young professionals. This includes assistance in obtaining retraining, if necessary, and the provision of jobs to certain categories of citizens.
- Constantly rising unemployment. It is connected not only with the lack of free jobs, but also with the frequent refusal of young people to work for a small wage.
- The presence of a small number of jobs for young people.
- Lack of demand for those professions that most students receive.
- Lack of necessary experience and seniority among potential employees.
The labor market and professions for young professionals
Currently, the Russian government has begun to pursue an active policy in the labor market. Its main goal is to help young professionals who have lost or have not yet found a job. This policy is accompanied by a number of activities:
- Help young professionals find work through commercial and public employment services.
- Assistance to young entrepreneurs in the form of subsidies and loans for business development, as well as training, advice and preferential tax burden on established enterprises.
- The state in every possible way contributes to the development and expansion of the system of vocational training, as well as retraining. At the same time, employers are encouraged to participate in these programs. Thus master new profession or you can undergo retraining on an existing one, not only with the help of government programs training, but also directly at the enterprise.
- State protection of weakly protected sections of the population. The youth is one of them. For them, the government provides for job quotas, training for new professions, and also guarantees additional protection when hiring or firing.
- Public works that contribute to the creation of new jobs.
Youth labor market and its specifics
Like other labor markets, the market for young professionals has its own specifics.
- First, it is an unstable supply-demand ratio. First of all, it is due to the professional uncertainty of young people and constant changes in their desired orientation.
- Secondly, in recent years, a significant decrease in the number of young people employed or in training has been observed in our country. And the number of unemployed or nowhere students is constantly growing.
- Thirdly, the demand for inexperienced personnel tends to decrease. Since highly qualified and experienced specialists are more in demand. And they belong to a different age group.
- Fourth, women's employment is in a rather difficult situation. Employers increasingly began to prefer male youth as potential employees of their companies.
- And fifthly, the lack of demand for those professions for which young people are trained. Therefore, they have to undergo retraining and get a profession that is far from their original one. A lot of cases are also connected with the dissatisfaction of young people with their position. Because of this, quite a few young cadres quit their jobs and start looking for a more suitable one for their needs.
The labor market and young professionals through the eyes of employers
 Most employers are trying to hire experienced professionals with experience who know all the intricacies of a particular profession. In addition, in their opinion, it is quite difficult for young specialists to adapt to new conditions for them, namely, to an eight-hour working day, to the team and, in general, to the entire work process. However, there are many companies in Russia that are happy to hire specialists without experience, but most often the positions offered do not meet the expectations of applicants.
Most employers are trying to hire experienced professionals with experience who know all the intricacies of a particular profession. In addition, in their opinion, it is quite difficult for young specialists to adapt to new conditions for them, namely, to an eight-hour working day, to the team and, in general, to the entire work process. However, there are many companies in Russia that are happy to hire specialists without experience, but most often the positions offered do not meet the expectations of applicants.
This neglect of young professionals is due to several reasons:
- Spending a lot of time on training a university graduate and getting used to the organization itself. At first, it must be constantly monitored, comments should be made about incorrectly performed work, and subsequently corrected errors should be checked. And it is much easier for an employee with experience to start performing his duties, since he does not require special training and has an idea of the specifics of the work ahead.
- If the future employee is still at the stage of studying at an educational institution, then the employer has a prejudice about the regular sessions for which he will be obliged to let him go. In this situation, you will have to constantly look for a replacement for the absent employee, and in some cases even pay for the student leave of a young specialist.
- Among other things, the employer is often not sure about the choice of such an employee, and this uncertainty is fully justified. Having worked for a certain amount of time in a company, an employee, having gained experience, can easily leave for a more promising and paid job, thereby creating another headache regarding the search for a new specialist. In addition, young people at this age often start families, so if we are talking about a girl, then the employee may also soon go on parental leave early.
If we do not take into account all the fears of employers associated with hiring young professionals, we can also highlight the positive features in this matter, namely:
- Sincere desire to work and great diligence. Young specialists, having entered their first job, try to prove themselves as quickly as possible and get the location of the boss. They make a lot of effort to do their job as efficiently and quickly as possible, which cannot be said about employees who are already overwhelmed by the work routine.
- Non-standard thinking of graduates. Young people are characterized not only by ambition, but also by creative approaches to their work. Therefore, such specialists are able to bring a lot of new things to the work of the company, which can significantly affect its development.
- Possibility to set a small size wages. Since young specialists are well aware that no one will pay them much at the beginning of their career, they are ready to accept any job just to gain the necessary experience in work book. Employers, in turn, are not inclined to pay high salaries to specialists without relevant experience.
The youth labor market is the most problematic area of the state. Currently available higher education is no longer considered a guarantee of obtaining a prestigious, highly paid job.
The problem of employment of young specialists in a market economy is very relevant, as evidenced by the materials below from one of the most popular employment portals - www.hh.ru.
Being a young or "starter" specialist looking for an attractive job in the real sector of the economy is currently difficult. After all, who is a "young specialist"? First of all, this is a person with a certain baggage of theoretical knowledge, who has just received a diploma. Unfortunately, no more than 30% of graduates today can boast of practical experience in their specialty by the time they receive their diploma. When faced with the task of finding a job, the remaining 70% see the following in job descriptions: "Required work experience from 1-1.5 years". A reasonable question arises: where can I get this experience if I am a young specialist? Last years there is an active discussion (both within the universities themselves and among employers) how to evaluate a student candidate who combines work
and study. And there can't be one right answer. There are those who successfully combine study with work, strengthening their professional knowledge, and there are those who, on the contrary, fully devote themselves to the process "earnings" money, putting their education on the back burner. This is a conscious choice of everyone and it can consist of the following important steps .
First, you need to determine what is the main goal - gain practical experience in their specialty or "making" money. The first option, most likely, will lead to a large company, where even in a crisis period, the possibility of internships or work in a position remains "Department Assistant". For example big company it is easier to describe a career path for a young specialist. For example, it might be: Department Assistant -> Department Specialist -> Lead Specialist -> Team Leader -> Department Head -> Department Head. The second option is more likely to lead to a small company, where, due to the extended functionality, there will be a real opportunity to earn money, but, unfortunately, it is difficult to predict a career path, since with related functionality, it is possible to gain practical experience in a completely different specialization.
Secondly, you should evaluate the real level of your knowledge and skills in order to determine which companies it makes sense to pay attention to. Unfortunately, many graduates ignore the requirements specified in the job description, such as the level of knowledge of a foreign language, various specialized programs, although this is critical when applying for a job. Thus, they cut off their path to this company. In this case, it will be more correct, but also more difficult, to acquire these skills. For example, your resume should include: "The level of knowledge of the English language pre-intermediate
(under study)".
Thirdly, it is important to define a list of resources for finding a job. These can be leading recruiting agencies that are engaged in the employment of young professionals, key Internet portals, etc.
Fourth, we should not forget about another very important factor - factor of "burning eyes". Employers have been talking about it more and more lately. The employer expects to see not only one hundred percent compliance with the requirements of the vacant position, but
and sincere interest in working in this particular company. This can be demonstrated in an elementary way: pre-prepare for an interview by browsing online sources and collecting recommendations
about the company from acquaintances working in it, etc.
In addition, to prevent problems in employment
and obtaining any attractive job with formal employment, it is necessary to understand the following very clearly.
Firstly, due to which you will be able to constantly bring profit to the future employer, since with market economy:
- it is profit making that is the main goal of any extrabudgetary economic entities(JSC, CJSC, LLC, etc.);
– to pay you wages any non-budgetary organization or individual entrepreneur can only at the expense of the profits received as a result of your activities (usually
as a result of providing sales of any goods and services), since they have no other sources for self-financing, and your salary will necessarily be much less than sales volumes (especially if any material goods are sold, and not computer programs, an Internet connection or cable TV etc.), since large financial costs are required to ensure economic activity given legal entity, paying salaries to other employees and making a profit for the owner.
Secondly, how can you convince any employer in the real sector of the economy that if you are hired, he will quickly begin to receive financial benefits and will not have any problems, i.e. you are already prepared for a successful job or you can quickly enter business and make a profit. This is especially important for the official employment of girls and women in any non-budgetary organizations, since in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation, pregnant women and those with children under a certain age are protected from dismissal, so if they do not earn their wages, the employer will still have to pay it or have problems in the future.
Thirdly, it is advisable to decide by the time of employment, so as not to waste time, what kind of work you want to get, since only two options are really possible:
- a job in which you are directly involved in the sale of goods and services and as a result receive your percentage of sales as a salary (when selling real goods, it is usually several times less than when selling services, since in the latter case the costs and risks much lower than any employer);
- work in budgetary or non-budgetary organizations that is not related to the direct sale of any goods and services by you.
The main requirement that employers impose on potential employees is the presence of successful work experience in similar positions. But where can he come from if a young specialist has just graduated from a university?!
Some students start working from the first courses. It is very difficult for a full-time student to find a job, because most employers prefer to hire not only accomplished specialists, but also those who are able to work full time,
and, if necessary, to be delayed beyond the set time.
And yet, all interested students can find a job related to obtaining skills and work experience in their specialty.
One of the options for such work can be described in the educational and training work on contractor agreements in the created TSPU named after. L. N. Tolstoy in accordance with federal law dated 02.08.2009 No. 217-FZ to an innovative company - LLC Innovative-Innovative Training and Production Enterprise "Energy Saving, Life Safety, Economy" (abbreviated as LLC IVUPP "EBZHE").
When looking for a job, keep in mind that companies have different attitudes towards the prospect of hiring specialists without work experience. Some still consider it a waste of time, while others, on the contrary, see an undeniable advantage in hiring, training and subsequent development of yesterday's graduates. In any case, the employment of some graduates is hindered by the fact that, as noted on the www.hh.ru portal, the situation is already becoming a trend in which:
- students often cannot adequately evaluate themselves, overestimating their attractiveness for employers in the labor market;
- students and young professionals without work experience, at best, with only a higher education, are trying to impose their conditions on the employer. Excessive ambitions and the desire to get everything at once are not the key to success in finding a job. Therefore, experts advise when looking for a job to be guided by real knowledge and skills, and not by the desire to earn as much as possible, and not to overestimate your financial expectations.
Graduates who start working in their student years tend to be more successful in their careers than those who start
looking for a job after graduation. It is easier for them to make a career, because by the time they receive a diploma, they are already laying a solid foundation for the future. The ideal option is when a senior student comes to the company and, working part-time, gets his first professional experience. There is such an opportunity for all interested students.
Labor market research in Moscow
The study was prepared on the basis of a statistical analysis of 48,032 vacancies and 218,364 resumes posted on the websites site, joblist.ru and career.ru in 2008-2011.
The study contains:
- General dynamics of the labor market for young professionals;
- the structure of demand for specialists in professional fields;
- structure of demand for specialists by type of education;
- rating of mentioning universities and salaries in vacancies;
- most salaries analysis popular professions in the area under study;
- analysis of the scarcity of the most demanded professions in the studied area (hh.index);
- portrait of a young applicant;
- rating of fashionable professions for a young specialist;
- analysis of the concept of "successful career" for a young specialist.
Main conclusions:
- for three years, the number of vacancies for young professionals has almost doubled;
- young specialists were more seriously affected by the crisis - in the 1st quarter of 2009, the demand for them decreased by 79% compared to the 1st quarter of 2008;
- most of the vacancies for young professionals are placed in the professional areas "Sales" (21% of vacancies), "Administrative personnel" (18%) and " Information Technology" (12%).
- the most demanded among young specialists is economic education;
- the most mentioned university is Moscow State University. Lomonosov and MSTU im. N. E. Bauman;
- the level of salaries in the studied area is most sensitive to changes in the economy. For example, the salary of a department assistant in the 1st quarter of 2008 amounted to almost 33 thousand rubles, in the 1st quarter of 2009 - about 28 thousand rubles, and in the 1st quarter of 2010 - only 26 thousand rubles. At present, the income of this specialist has grown slightly and has almost reached 30 thousand rubles.
- junior programmers are the most scarce for the employer. There are about 1-2 people per vacancy;
- PR-manager, photographer and designer are the most fashionable professions, according to students;
- most students in 5 years see themselves as specialists in one of the large companies;
- comfortable working conditions and material wealth are the main synonyms for a "successful career";
- students consider part-time jobs and good studies to be the main way to build a successful career;
- For the sake of a successful career, students are ready to sacrifice only their free time.
The labor market in the field "Start of a career / Students"
The category of young specialists and students is one of the most unprotected in the labor market. In the midst of the crisis, at the beginning of 2009, the number of vacancies for young professionals and students decreased by 79% compared to the 1st quarter of 2008. Recovery in the labor market for young professionals was outlined just a year ago, in the 2nd quarter of 2010, when demand exceeded the pre-crisis level by 26%.
In 2011, the labor market for young professionals entered an active phase of growth, over the past two quarters outpacing the labor market as a whole in terms of growth rates.
In total, the share of vacancies for young professionals and students now accounts for about 5%, i.e. every 21st vacancy. For comparison: in the 2nd quarter of 2009, only every 75th vacancy was suitable for a young specialist or student.

The structure of demand for professional fields varies slightly from year to year. One can only note a shift in demand for young professionals from the "Administrative personnel" sector towards sales and IT specialists. Currently, the share of vacancies in the "Sales" sector accounts for 21% (9 percentage points more than in 2008), the "Administrative personnel" sector - 18% of vacancies (5 percentage points less) and IT -sphere - 12% (2 percentage points more).
In general, the top 10 professional areas account for almost 90% of all vacancies in the labor market for young professionals.
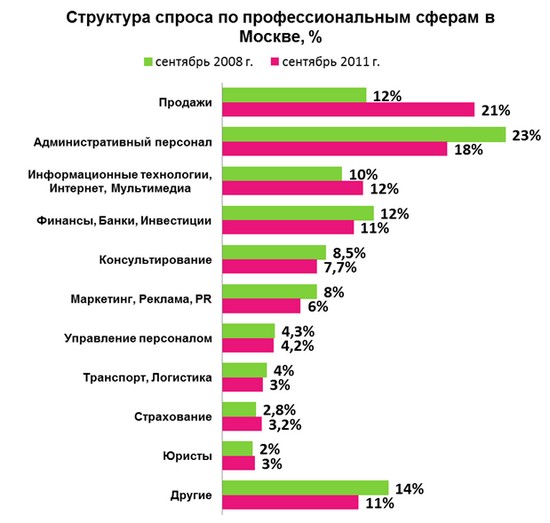
The most popular required education for young professionals is economics. The share of vacancies with the mention of such education accounts for 36%. Demand for young professionals financial education accounts for 24% of the total number of vacancies. Technical specialists are interesting in 22% of vacancies.
Less popular are specialists with mathematical education - 7%. The share of other types of education accounted for 10% (these are legal, sociological and linguistic education).

The most popular universities that are found in vacancies are Moscow State University. Lomonosov (23% of all vacancies), Moscow State Technical University. N. E. Bauman (18%), MEPhI (13%), Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (11%) and MAI (5%). The top 5 universities accounted for about 70% of all vacancies in which the name of the university was mentioned.
Less popular were SU-HSE and MESI (4% each), MPEI (3%), GUU, MADI, MTUCI, MISI-MGSU, MIREA, PRUE. GV Plekhanov (2% each) and MATI (1%).
On the high salary MAI students and graduates can count - more than 40,400 rubles. The level of salaries in which the mention of MADI is found amounted to exactly 40,000 rubles. Representatives of REU them. G. V. Plekhanov is offered an average of 39,200 rubles, State University - Higher School of Economics - 37,700 rubles, Moscow State University - 35,800 rubles.
The least (among the mentioned universities) are paid to students and graduates of the State University of Management - 26,900 rubles, MTUCI - 27,500 rubles. and MSTU im. N. E. Bauman - 33,300 rubles.


During the crisis, the level of salaries of many young professionals declined. The salary of a junior programmer in the 1st quarter of 2009 decreased by almost 15,000 rubles. compared with the 1st quarter of 2008, the salary of a sales manager - by 3,000 rubles, a department assistant - by 5,000 rubles.
Now the market is seeing a recovery in salaries, but not in all positions. Thus, the salaries of department assistants and junior programmers have not yet reached the level of the 1st quarter of 2008.


Currently, expected salaries for the position of junior analyst are 26% higher than the salaries offered. Expectations for junior lawyers are 24% higher, and sales managers and department assistants are 17% higher. The difference between the expected and offered salaries of a junior engineer is smaller - only 12%. The offered and expected junior programmer salaries are the same. 
One of the scarce specialists in the labor market for students and young professionals is a junior programmer (less than 2 people per vacancy). The highest competition in employment is for the position of junior engineer (6 people per position).

In addition to professions that are scarce and in demand on the labor market for young professionals, there are so-called "fashionable" professions that have become popular quite recently. According to an online survey conducted by the job search portal career.ru on August 9-16, 2011, PR-manager became the most fashionable profession among students (27% of the respondents noted it). The top three was closed by a photographer and a designer.
In addition, HR-manager, art director, programmer, blogger, stylist, fashion-editor and model got into the top ten fashion professions.

The portrait of a young specialist has changed slightly over the past three years. Most candidates have no work experience, have basic knowledge of English and expect to receive 20-30 thousand rubles.
It is noteworthy that now women are more actively looking for work: they account for 59% of all resumes, while three years ago - only 38%.
| Portrait of a young job seeker | 2008 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|
| Floor | ||
| male | 62% | 41% |
| feminine | 38% | 59% |
| Education | ||
| Higher | 42% | 49% |
| The average | 58% | 51% |
| Ownership English language | ||
| don't know | 11% | 11% |
| basic knowledge | 46% | 48% |
| read professional literature | 11% | 12% |
| I can do an interview | 14% | 14% |
| Speak fluently | 17% | 15% |
| experience | ||
| No experience | 74% | 76% |
| From 1 year to 3 years | 23% | 19% |
| 3 to 6 years old | 3% | 3% |
| Over 6 years | 1% | 2% |
| Salaries | ||
| 5-10 thousand rubles | 3% | 2% |
| 10-15 thousand rubles | 12% | 7% |
| 15-20 thousand rubles | 25% | 20% |
| 20-30 thousand rubles | 43% | 45% |
| 30-40 thousand rubles. | 12% | 20% |
| 40-60 thousand rubles | 5% | 6% |
| 60-80 thousand rubles | 0% | 0% |
| 80-100 thousand rubles | 0% | 0% |
| 100-300 thousand rubles | 0% | 0% |
| More than 300 thousand rubles. | 0% | 0% |
Basic requirements for young professionals
- Higher / incomplete higher education / final year student
- Excellent theoretical knowledge of their own and related fields
- Preferably an internship or internship
- Good knowledge of a foreign language
- Excellent PC knowledge
- Work experience required
- Age from 20 years
- Teamwork skills
- Ability and desire to learn
- Additional qualifications required
- Responsibility
- Stress tolerance
- Accuracy, attention to detail
According to an online survey conducted by the job search portal career.ru on July 5-12, 2011, 40% of the young professionals surveyed see themselves as a specialist working in a large company in 5 years. About 35% expect to lead a department in the company in 5 years. About 14% believe that they will have their own small business, and only 3% see themselves as the big boss.

For many respondents, successful work means comfortable working conditions and material wealth (53%), for 26% of young professionals it means managerial position, and only for 17% - a high salary.

Most of the respondents to build a successful career work part-time (65%), and also study well (63%); slightly fewer respondents pay attention to additional subjects (41%) and make connections in the business environment (31%).
It is worth noting that every 15th student does nothing to build successful career.

To build a successful career, the majority of respondents are willing to sacrifice free time (85%). Significantly fewer people are willing to sacrifice family time (28%) and money (27%). About 7% of respondents are not ready to sacrifice anything for a successful career.

*multiple answers allowed
Speaking about the labor market, it should be noted that this market interacts with other markets operating in the national economy of the country, so it also has disadvantages. economic system country as a whole. The current situation, which is Russian market labor is quite stressful. The scale of registered and hidden unemployment is growing, and its duration is increasing. In January-February 2016 alone, unemployment increased by 0.3% (from 5.5% to 5.8%). This situation affects all groups of the working-age population, but most acutely - in the least protected layers of the labor force, which include young people in general and young professionals in particular. Although young people in all countries of the world are considered vulnerable in the labor market, in Russia the outbreak of the crisis makes this phenomenon more acute.
According to Rostrud data for 2015, 30.5% of all Russian unemployed are young people under the age of 29. The need to analyze the situation of young people in the Russian labor market is determined by two important circumstances. Firstly, young people make up about 35% of the working-age population of Russia, and secondly, young specialists are the future of the country's economy, and its subsequent development depends on the starting conditions for their activities.
The characteristics of the market for young professionals differ significantly from the labor market of other groups of the population, both in terms of quantitative and qualitative parameters: high unemployment, low wages, high tension in the labor market in a large number of industries and regions. Currently, the following problems can be identified in the labor market of young professionals in Russia:
1. Imbalance of supply and demand in the labor market. This is due to the discrepancy between the profiles and volumes of training of specialists in certain specialties with the requirements and needs of the modern labor market.
2. Rising unemployment, which is associated not only with the lack of vacancies, but also with the low level of wages offered.
3. Lack of necessary experience for potential employees.
4. Insufficient practical and often theoretical training and, consequently, qualifications of university graduates.
In order to find out how stable and comfortable entry-level specialists feel in the labor market, HeadHunter Research Service used a “well-being index”, which includes a survey on the following indicators: assessment of stability at the current place of work (there is a threat of dismissal); assessment of the difficulty of finding a job; assessment of the criticality of job searches; willingness to reduce salary claims; assessment of the chances of finding a job in the near future. The results of the study showed that the general trend of sentiment in the Russian labor market for young professionals at the end of 2015 remains negative, with a deterioration in sentiment in all indicators compared to 2014.
Most employers try to hire, first of all, experienced professionals with experience who already know all the intricacies of a particular profession. In addition, in their opinion, it is rather difficult for young professionals to quickly adapt to new conditions for them, namely to the working day, to the team and to the work process in general. Nevertheless, there are many companies in Russia that are ready to gladly hire specialists without experience, but in this case, most often the offered positions do not meet the expectations of applicants. If we talk about the share of vacancies for young professionals in Russian cities, then in Moscow in 2014, vacancies for young professionals accounted for a little more than 9% of the total demand in the region (or every 11th vacancy in the labor market in Moscow). In St. Petersburg, only every 14th vacancy was focused on a young specialist, in Rostov-on-Don and Samara - every 18th, in Yekaterinburg and Omsk - every 19th, in Novosibirsk and Perm, only every 22nd vacancy .
There are several reasons for such an attitude towards young professionals: Expenses of additional time for additional training of a university graduate and adaptation in the organization. A young specialist needs to be taught the use of theory in practice, professional subtleties and norms of behavior required for implementation. labor functions. It is not economically profitable for an employer to hire an employee who is still at the stage of training at an educational institution. In this situation, you will have to periodically look for a replacement for the absent employee, and in some cases pay for student leave of a young person who is studying. The employer is often not sure about the choice of such an employee, and this uncertainty is fully justified. Having worked for a certain amount of time in a company, an employee, having gained experience, can easily leave for a more promising and highly paid job, thereby creating another "headache" regarding the search for a new specialist. It is no coincidence that people who have worked in the company for less than a year are most often fired.
But we can highlight the positive characteristics of young professionals, namely:
1. Sincere desire to work and great diligence. Young specialists, having entered their first job, try to prove themselves as quickly as possible. They make a lot of efforts to do their job as efficiently and quickly as possible, which cannot be said about some employees with great experience and work experience.
2. Non-standard thinking of graduates: young people are characterized not only by ambition, but also by creative approaches to their work - they are able to bring a lot of new things to the work of the company, which can significantly affect its development.
3. Possibility to set low wages for this category of workers. Many young professionals are well aware that at the beginning of their career no one will pay them much, they are ready to accept any job just to gain the necessary experience.
4. When experience is added to theoretical training, an excellent worker can come out of a beginner. Sometimes there is even a chance to bring up a like-minded person and a follower focused specifically on this company, familiar with its specifics and corporate culture.
Among the requirements for young professionals, employers indicate that the candidate for the position has the following knowledge and skills: competent speech, PC knowledge; ability to analyze, work with a large array of data. This list may vary and be supplemented depending on the professional field, but the most important thing is that young specialists should know the range of issues that they have to solve and be able to have the qualifications sufficient to fulfill them. According to employers, a young specialist should also have the following qualities in his character: stress resistance, active life position, focus on results, efficiency, quick adaptation, initiative, responsibility, confidence and self-organization.
This study of the labor market of young specialists also includes a study of the structure of their demand by branches and spheres of the country's national economy. So in Novosibirsk, most of the vacancies in 2014 in the Career Start/Students area were posted in the Sales, Administrative Staff and IT, Internet, Multimedia specializations - about 52% of the total number of vacancies posted in this area . And the leader was "Sales" - 29.4% of vacancies from the total demand. A similar picture of demand is observed in other large cities of Russia: Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Rostov, etc. Also in the top popular specializations are the categories "Administrative personnel", "Consulting", "IT, Internet, Multimedia" and the banking sector. These areas are popular due to the fact that they are available by qualification mainly to young, energetic specialists with little work experience, and do not require serious professional training at the initial stage. Least of all vacancies were posted in such specializations as "Production of raw materials", "Lawyers" and "Medicine, Pharmaceuticals", since these areas require a high level of education, a large length of service and work experience.
The problems under consideration in the labor market of young professionals require legislative and other measures both in the national economy as a whole and in the field of education: by adapting the education system to the needs of large and medium-sized enterprises-employers. To do this, we need to consider the question joint work educational institutions and employers to prepare new standards for vocational education.
In turn, students should not remain aloof from this issue, they should have a greater desire to obtain and improve high-quality knowledge and skills in the professional field. Young people should consciously approach the choice of their future profession, and the school should also contribute to this solution of the problem.
Bibliography
1. Khabarov V.I., Khabarova O.G. A modern view of human resource management in a branch university from the standpoint of knowledge management. - Collection scientific articles based on the results of the International Scientific practical conference: Institutions and Mechanisms innovative development in economics, project management December 27-28, 2013 in St. Petersburg. - St. Petersburg: Publishing House "KultInformPress", 2013. - p. 151-152.
2. Khabarova O.G., Khabarova K.V. The influence of the transport factor on the efficiency of the use of labor resources in a large locality. – Collection of scientific articles based on the results of the International Scientific and Practical Conference February 13-14, 2015, St. Petersburg. - St. Petersburg: Publishing House "KultInformPress", 2015. - p. 189-191.
3. Khabarova O.G. Human Resources Management: Guidelines. Novosibirsk: Publishing House of SGUPSa, 2011 -20p.
4. Economics of labor resources: Tutorial for universities. Ed. P.E. Shlendera.- M .: Vuzovsky textbook, 2011 - 302 p.
Popov Andrey Vasilievich, Junior Researcher, Institute for Socio-Economic Development of Territories of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vologda, Russia
A Young Professional on the Labor Market: Labor Demand and education Quality (Evidence from Vologda Region)
|
Territory |
Year |
2014. |
|||
|
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2014 |
||
|
The Russian Federation |
37,2 |
41,9 |
42,4 |
40,3 |
108,3 |
|
Northwestern Federal District |
34,9 |
40,6 |
41,5 |
36,7 |
105,2 |
|
Saint Petersburg |
30,2 |
35,6 |
40,3 |
43,7 |
144,7 |
|
Kaliningrad region |
28,3 |
36,9 |
32,1 |
33,5 |
118,4 |
|
Republic of Karelia |
37,3 |
39,5 |
37,0 |
34,0 |
91,2 |
|
Vologda Region |
38,6 |
36,5 |
37,9 |
32,7 |
84,7 |
|
Novgorod region |
37,6 |
33,5 |
39,1 |
30,2 |
80,3 |
|
Pskov region |
35,2 |
42,9 |
35,3 |
38,3 |
108,8 |
|
Komi Republic |
30,3 |
44,3 |
52,4 |
39,2 |
129,4 |
|
Leningrad region |
41,3 |
38,5 |
41,5 |
38,7 |
93,7 |
|
Murmansk region |
34,3 |
49,9 |
48,6 |
33,5 |
97,7 |
|
Arhangelsk region |
40,1 |
43,6 |
46,6 |
36,9 |
92,0 |
Picture 1.Unemployment rate in the Vologda Oblast by age groups, %

Note: color 1- excess of own labor resources over the needs of the region; color 2– current and prospective demand for workforce closed at the expense of citizens of retirement age; color 3– in the medium term, a shortage of personnel is possible
Figure 2.Cartographic scheme of the provision of labor resources of the municipalities of the Vologda Oblast
Selection characteristics
According to the survey, when hiring, employers first of all pay attention to such aspects as: work experience (56%), compliance of the education received by the applicant with the requirements of the profession (55 %), recommendations from the previous place of work (48 %). Marital status, the presence or absence of children, as well as appearance do not play a significant role in employment (table 2).
The current practice of selecting applicants has led to the fact that the need for young workers is quite moderate (table 3). The deficit is experienced by only 13% of economic entities. In this sense, the Kirillovsky district stands out, where there is an acute need for young personnel among 38% of organizations. Moderate demand was found in 55% of the enterprises of the Syamzhensky district. In the rest of the districts, most organizations noted that they had little need for an influx of young professionals.
table 2
Distribution of answers to the question “When applying for a job, do you first of all pay attention to...?”, in %
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
Vytegorsky |
||
|
Work experience |
48,4 |
33,3 |
51,5 |
52,1 |
74,1 |
55,6 |
|
Compliance of the education received by the applicant with the requirements of the profession |
45,2 |
61,9 |
57,6 |
61,6 |
46,6 |
54,6 |
|
51,6 |
47,6 |
63,6 |
46,6 |
39,7 |
48,1 |
|
|
Higher education |
29,0 |
28,6 |
12,1 |
24,7 |
12,1 |
20,4 |
|
Health status |
23,8 |
42,4 |
16,4 |
12,1 |
19,0 |
|
|
Availability of certificates, certificates and other documents confirming the existence additional education |
14,3 |
12,1 |
19,2 |
24,1 |
17,6 |
|
|
Age |
29,0 |
23,8 |
11,0 |
20,7 |
17,1 |
|
|
Appearance, charm |
15,5 |
|||||
|
Presence / absence of children (for women) |
||||||
|
Marital status (married/married, single/single) |
||||||
|
Other |
||||||
Source:compiled by the author
Table 3
Distribution of answers to the question “How badly does your organization need young workers (under 30)?”, in %
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
|||
|
The organization is experiencing a shortage of young workers |
37,9 |
18,2 |
12,4 |
|||
|
There is a moderate need |
24,1 |
55,0 |
18,2 |
34,3 |
24,1 |
29,5 |
|
The organization's need for young personnel is negligible |
27,6 |
30,0 |
27,3 |
41,4 |
41,4 |
36,2 |
|
Difficult to answer |
10,3 |
10,0 |
36,4 |
18,6 |
27,6 |
21,9 |
Source:compiled by the author
When selecting young employees, employers first of all pay attention to such quality characteristics as: professional competence (44%), developed personal and business qualities(28%), work experience in the specialty (23%), knowledge of the specifics of the organization's activities (21 %) and the basic level of computer literacy (16 %; figure 3). Experience research work, knowledge foreign languages, the level of performance in educational institutions and the presence of a diploma from a prestigious educational institution do not play a special role (1-3%).
 Figure 3 Distribution of answers to the question "Please rate the importance of various criteria in the selection of young workers (under 30) for your organization?", answer option "very important", in %
Figure 3 Distribution of answers to the question "Please rate the importance of various criteria in the selection of young workers (under 30) for your organization?", answer option "very important", in %
Source:compiled by the author
One of the possible reasons for the lack of active demand for young professionals is the low level of professional training - this problem has been repeatedly confirmed by many studies. (Bondarenko, 2005; Vorobieva, Chashchin, Mineeva, 2008; Nechaeva, Vakulenko, 2015; Nikulina, 2011). Let us consider employers' assessments of the quality of training of young personnel hired by them.
According to employers, the quality of training of young workers at the time of their employment is at a fairly high level (table 4). The most developed are the skills of working in a team (3.7 points out of 5 possible), the ability to retrain, readiness to improve the professional level and discipline (3.6 points), and the least - basic computer literacy, as well as initiative and creativity in work ( 3.2 points). In territorial terms, the opinions of employers have some differences. So, in the Kirillovsky district, the level of culture and discipline are highly valued, in the Syamzhensky and Gryazovets districts - the ability to work in a team and the ability to retrain, in Vytegorsky and Kharovsky - discipline and teamwork skills.
Table 4
The quality of training of young workers at the time of their employment, points
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
Vytegorsky |
||
|
Ability to work in a team, communication and understanding skills |
||||||
|
Discipline, performance |
||||||
|
Ability to relearn, willingness to improve professional level |
||||||
|
General education skills (grammar, math, etc.) |
||||||
|
General culture level |
||||||
|
Basic professional skills required for this position |
||||||
|
Basic computer literacy, usage skills software |
||||||
|
Initiative, creativity |
||||||
Source:compiled by the author
The highest quality of training is possessed by young workers with higher and secondary vocational education, and with an increase in the level of education, according to employers, the quality of graduate training also increases. (table 5 ) . The exception is the Kirillovsky district, where the opposite trend was noted: the assessment of the quality of training of young specialists with secondary and primary vocational education is significantly higher than with higher education.
Table 5
Quality of training for young addiction workers
on the level of their education, points
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
Vytegorsky |
||
|
Initial vocational education |
||||||
|
Secondary vocational education |
||||||
|
Higher professional education |
||||||
Source:compiled by the author
As practice shows, sometimes employers are faced with the problem of a mismatch between the qualifications of graduates and the work they perform. (Antropov, 2013; Glotova, 2014; Kazimov, 2013; Nikulina, 2011). And more often, professional preparedness turns out to be lower than required, the problem of “over-education” is much less common.
Since, in general, employers assess the quality of training of young workers quite highly, their qualifications, in their opinion, most often meet the requirements of jobs. (table 6 ) .
However, there is concern about the high proportion of those whose training is below the required minimum. This fact was noted in 22% of business entities. This situation is most typical for the Kharovsky district (67%), and least for Kirillovsky (6%).
Table 6
Distribution of answers to the question: “To what extent does the qualification (training) of young workers correspond to the work they perform?”, in %
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
Vytegorsky |
||
|
Higher than required job can perform more skilled work |
11,8 |
|||||
|
Meets the requirements of the job (in order to perform more skilled work, they need to learn a little more) |
64,7 |
66,7 |
33,3 |
65,5 |
73,2 |
65,0 |
|
Less than what is required to get the job done |
20,0 |
66,7 |
22,4 |
17,1 |
22,4 |
|
|
Difficult to answer |
17,6 |
|||||
Source:compiled by the author
The list of reasons for the discrepancy between the professional skills of young workers and the requirements of jobs is quite diverse. (table 7 ) . The main source is the lack of necessary work experience (51%). Lack of motivation to quality performance job duties (21%), low level of professional training (17%) and labor discipline (12%). Moreover, in the context of districts, employers generally gave fairly similar assessments of the reasons for the mismatch of qualifications with the requirements of jobs.
Ultimately, the productivity of young workers is average (table 8 ) . This opinion is shared by more than 80% of employers. The highest estimates of labor productivity of young specialists were noted in Gryazovetsky and Kirillovsky districts (16 and 12%, respectively), the lowest - in Kharovsky district, where 17% of respondents described it as low.
Table 7
Distribution of answers to the question “In your opinion, what are the main reasons for the discrepancy between the professional skills of young workers and the requirements of jobs?”, in %
|
Possible answer |
District |
The average |
||||
|
Kirillovsky |
Syamzhensky |
Kharovsky |
Gryazovetsky |
Vytegorsky |
||
|
Lack of required work experience (minor work experience) |
32,3 |
52,4 |
30,3 |
56,2 |
63,8 |
50,5 |
|
Lack of motivation for quality performance official duties |
16,1 |
28,6 |
18,2 |
26,0 |
15,5 |
20,8 |
|
Low level of professional training in educational organization |
14,3 |
12,1 |
24,7 |
13,8 |
16,7 |
|
|
Low level of labor and performance discipline |
12,9 |
14,3 |
15,2 |
13,7 |
12,0 |
|
|
Low level of communication skills |
11,0 |
|||||
|
Inability to master new technologies |
||||||
|
Low level of organization of work and mastery of management methods |
||||||
|
Difficult to answer |
19,4 |
|||||
|
Other |
||||||

